Stop Mysql Macos
- MySQL Community Edition is a freely downloadable version of the world's most popular open source database that is supported by an active community of open source developers and enthusiasts. MySQL Cluster Community Edition is available as a separate download.
- MacOS 10.13 High Sierra - End of Life Support Ending January 31, 2021 Updated 11/18/20. On November 12, 2020, Apple released macOS 11, Big Sur. In keeping with Apple's release cycle, we anticipate macOS 10.13 High Sierra will no longer receive security updates starting in January 2021.
- For installation on macOS, including using both the binary package and native PKG formats, see Section 2.4, “Installing MySQL on macOS”. For information on making use of an macOS Launch Daemon to automatically start and stop MySQL, see Section 2.4.3, “Installing a MySQL Launch Daemon”.
Macos Stop Mysql
MySQL Community Edition is a freely downloadable version of the world's most popular open source database that is supported by an active community of open source developers and enthusiasts.
When you stop an instance, it remains stopped, and does not respond to application connections, until you start it again. Stopping an instance suspends instance charges. The instance data is unaffected, and charges for storage and IP addresses continue to apply. Note: You cannot stop a read replica instance. To stop an instance. Simple database development tool for MySQL and PostgreSQL environments. If yours is one of the majority of organizations migrating your existing commercial database to open source, such as MySQL or PostgreSQL, or if you’re building new in-house applications on open source database management systems (OSDBMS), then you know that commercial tooling for these databases falls short.
MySQL Cluster Community Edition is available as a separate download. The reason for this change is so that MySQL Cluster can provide more frequent updates and support using the latest sources of MySQL Cluster Carrier Grade Edition.
MySQL 8.0 is the most current GA release. Download MySQL 8.0 »
Learn What's New in MySQL 8.0 and view the Performance Benchmarks.
Online Documentation:
| Looking for previous GA versions? |
Please report any bugs or inconsistencies you observe to our Bugs Database.
Thank you for your support!
Contents
- Service Managers
- Starting the Server Process Manually
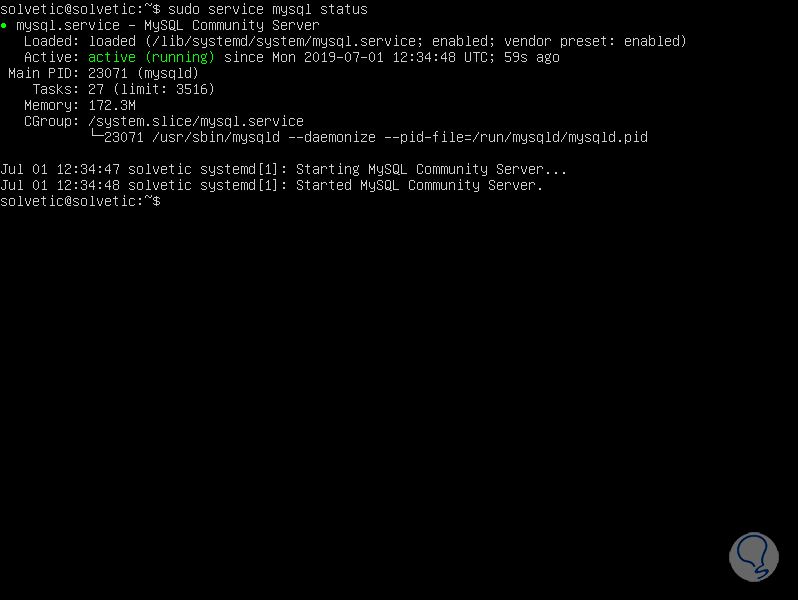
There are several different methods to start or stop the MariaDB Server process. There are two primary categories that most of these methods fall into: starting the process with the help of a service manager, and starting the process manually.
Service Managers
sysVinit and systemd are the most common Linux service managers. launchd is used in MacOS X. Upstart is a less common service manager.
Systemd
RHEL/CentOS 7 and above, Debian 8 Jessie and above, and Ubuntu 15.04 and above use systemd by default.
For information on how to start and stop MariaDB with this service manager, see systemd: Interacting with the MariaDB Server Process.
SysVinit
RHEL/CentOS 6 and below, and Debian 7 Wheezy and below use sysVinit by default.
For information on how to start and stop MariaDB with this service manager, see sysVinit: Interacting with the MariaDB Server Process.
launchd
launchd is used in MacOS X.
Upstart
Ubuntu 14.10 and below use Upstart by default.
Starting the Server Process Manually
mysqld
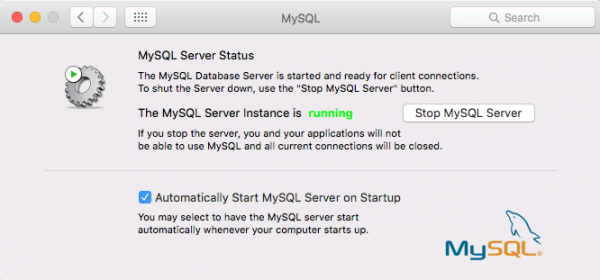
mysqld is the actual MariaDB Server binary. It can be started manually on its own.
mysqld_safe

mysqld_safe is a wrapper that can be used to start the mysqld server process. The script has some built-in safeguards, such as automatically restarting the server process if it dies. See mysqld_safe for more information.
mysqld_multi
Stop Mysql Macos Download
mysqld_multi is a wrapper that can be used to start the mysqld server process if you plan to run multiple server processes on the same host. See mysqld_multi for more information.
mysql.server
mysql.server is a wrapper that works as a standard sysVinit script. However, it can be used independently of sysVinit as a regular sh script. The script starts the mysqld server process by first changing its current working directory to the MariaDB install directory and then starting mysqld_safe. The script requires the standard sysVinit arguments, such as start, stop, and status. See mysql.server for more information.
Stop Mysqld Mac
Comments
Stop Mysql Mac